Greater China Deals Barometer Report: Dealmaking hits 3-month low in August

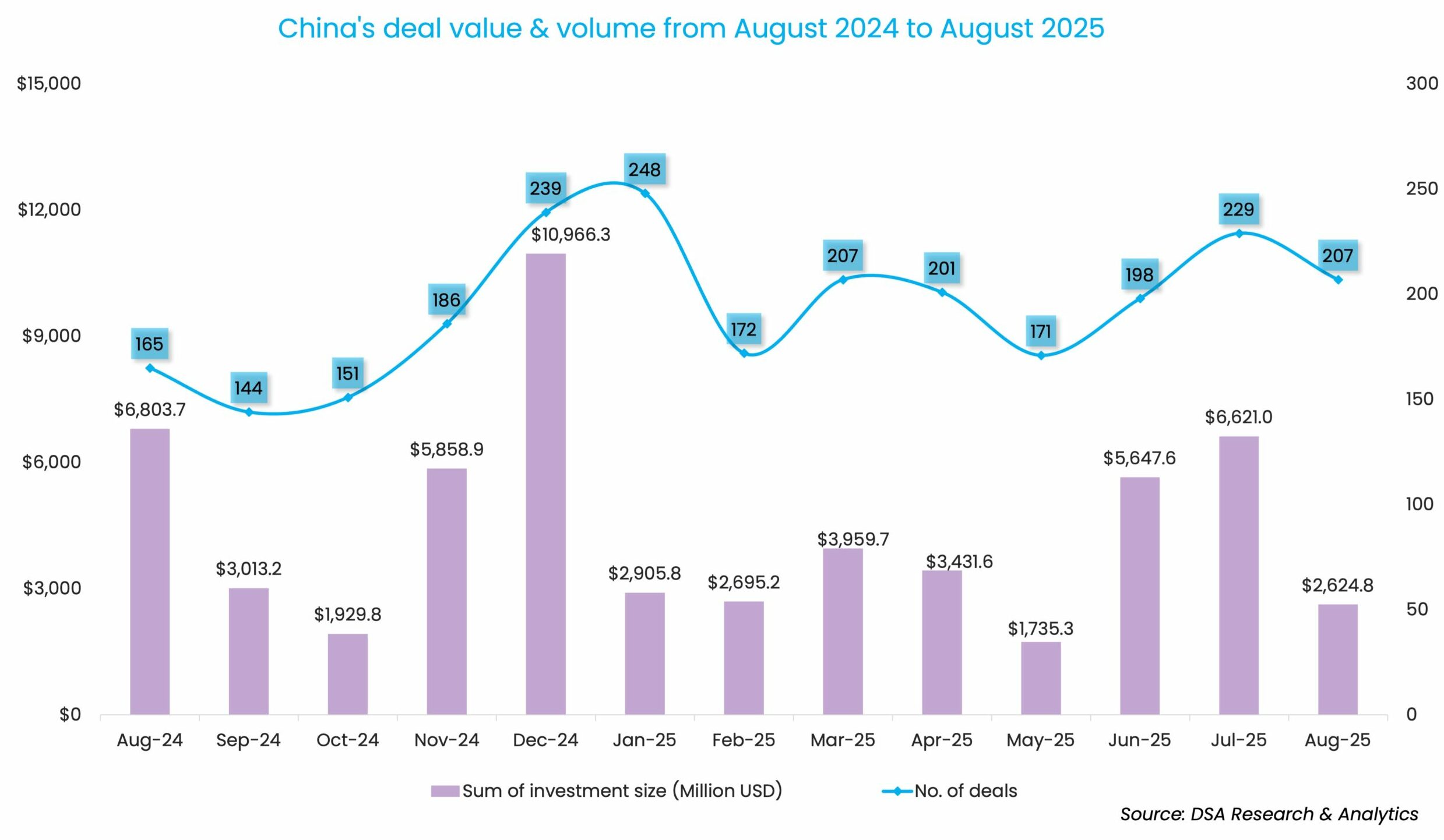
Investment activity in Greater China hit the brakes in August, with dealmaking plunging to its slowest pace in three months. The market saw just 207 deals closed, totaling $2.6 billion, a stark 60.4% drop in value and a 9.6% decline in volume compared to July.
Despite a V-shaped rebound from March to July, the venture funding scene is still far from the peak achieved a year ago. While August’s deal count edged 25.5% higher than the same month last year, the total value plummeted by 61%, a reminder that the high of 2024 is still out of reach, according to DealStreetAsia’s proprietary data.
In the first eight months of 2025, venture investors have invested a total of $29.6 billion through the completion of 1,633 deals. The deal value was 23.7% less than the same period in 2024, while the deal count was 9.7% more.
The sharp slowdown raises questions of whether the current dealmaking developments are just a temporary lull or a sign of caution gripping investors in the world’s second-largest economy, amid slow domestic economic growth and macro uncertainty.
A major cause for concern is that mainland China-focused private equity and venture capital funds have been struggling to fundraise. In the first half of 2025, only nine PE/VC funds managed to raise $350 million, a meagre portion of the $24.9 billion raised in the full year of 2024, S&P Global reported, citing data from Preqin. The fundraising decline bucked the global PE fundraising growth during the same period, the report added.
Top deal of the month
What sets August apart is that only three megadeals, or investments worth at least $100 million, were recorded. The top deal went to global logistics builder and investor GLP, which signed an agreement with Zhejiang government-affiliated entities in the month to invest a total of RMB 2.5 billion ($349.5 million) into GLP’s China data centre business.
HongShan-backed automotive electronic chip developer SiEngine Technology sealed its Series B funding round at over 1 billion yuan ($139.2 million), with the state investor China Structural Reform Fund II as the lead investor.
Minghui Pharmaceutical, a Chinese late-stage clinical biopharmaceutical company, was the third megadeal, which completed a pre-IPO financing of $131 million co-led by global healthcare investment firm OrbiMed and Qiming Venture Partners.
List of megadeals (August 2025)
| Company Name | Headquarters | Investment size (Million USD) | Unspecified size | Investment stage | Lead investor(s) | Other investor(s) | Industry/Sector | Vertical |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLP’s China data center business | Shanghai | 349.5 | Quzhou Industrial Holding Group | Business Support Services | N/A | |||
| SiEngine Technology | Wuhan | 139.2 | B | China Structural Reform Fund II | Automobiles & Parts | Electric/Hybrid Vehicles | ||
| Minghui Pharmaceutical | Shanghai | 131 | Pre-IPO | OrbiMed, Qiming Venture Partners | TF Capital, BioTrack Capital, 5Y Capital, New Day Fund, Wider Link Enterprise Investment | Pharmaceutical | N/A |
Early-stage investments dominated the funding scene. Series A and pre-Series A rounds accounted for 53.6% of the total deal count, clocking 30.9% of the deal value. Late-stage dealmaking saw a recovery with a total of four pre-IPO deals recorded in August.
Most recently, Nasdaq has proposed a set of new rules that require a minimum of $25 million public offering proceeds for new listings of firms principally operating in China, to bolster investor protection and market stability, the bourse said on September 3.
The proposed rule changes could make a dent in the small Chinese firms looking to go public on the Nasdaq bourse.
Three megadeals raise 23.6% of PE-VC money in Aug 2025

Chinese offshore IPOs rebounded in 2024 after a two-year slump, but the market was dominated by small-cap listings. The average deal raised just $50 million — down from $300 million in 2021 — as geopolitical tensions between China and the US, stricter Chinese regulatory oversight, and Beijing’s tighter controls on overseas fundraising kept blockbuster listings at bay, according to a report published by the US-China Economic and Security Review Commission (USCC) in March.
As of March 7, 2025, there were 286 Chinese companies listed across the top three largest US exchanges, with a total market capitalisation of $1.1 trillion. That valuation increased by $250 billion from the start of 2024, when this table tracked just 265 Chinese companies listed on U.S. exchanges with a total market cap of $848 billion, per the USCC.
HK’s tech ecosystem in the limelight
Apple’s key supplier, Foxconn Technology, made a strategic investment in Hong Kong-based robotics firm Robocore Technology in August as the world’s largest precision electronics manufacturer forayed into the smart robotics market.
Robocore’s funding added to the heightened investment interest in Hong Kong startups. A total of seven funding deals were secured in July, equal to the total number of deals closed throughout the first six months of 2024.
The city’s tech ecosystem has tracked an unprecedented influx of capital in the past three years, from the inception of Hong Kong Investment Corporation (HKIC), an investment firm wholly-owned by the Hong Kong government in 2022 with a total of HKD 62 billion ($8 billion) in capital, to the series of venture funds set up by local public universities.
The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) has been one of the early movers in its investment approach, with the launch of HK$500-million Redbird Innovation Fund (RIF) in April 2024 to provide anchor investments to GPs investing in HKUST-born projects.
In March, HKUST tied up with state-owned Shanghai Industrial Investment Holdings (SIIC) to establish a new fund targeting Hong Kong’s biotechnology and life science sector. The Hong Kong Biotechnology Fund (HKBF) will be the inaugural venture investment fund under RIF. The fund has a target size of HK$600 million ($77.2 million).
However, rigid and fragmented university licensing terms remain an issue hindering the growth of early-stage innovation in the city.
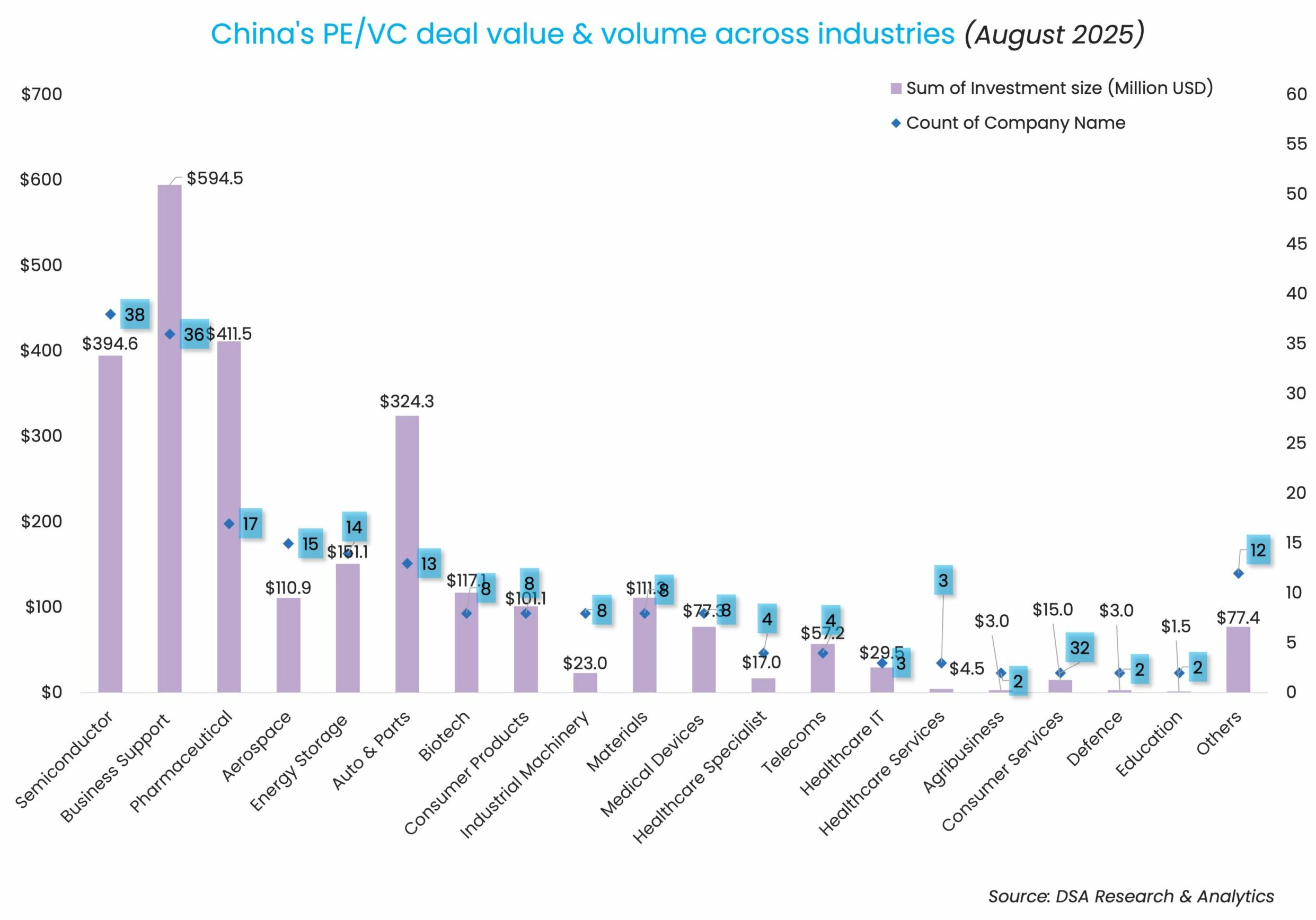
Sectorally speaking, business support services have overtaken semiconductor as the most-invested sector by value, largely thanks to the busy dealmaking scene for AI and robotics startups serving businesses.
The business support sector as a whole secured $594.5 million through the completion of 36 deals, while the semiconductor industry raised $394.6 million through 38 deals.
Qiming tops investor list
Chinese blue-chip venture capital firm Qiming Venture Partners invested $253.1 million across six deals, making it the most active investor of the month.
Founded in 2006, Qiming currently manages eleven US Dollar funds and seven RMB funds with $9.5 billion in capital raised. Since its inception, the firm has targeted early and growth-stage opportunities across the technology and healthcare sectors.
The month also saw the comeback of other top-tier VC firms, including 5Y Capital, which manages over $5 billion in capital from global investors. 5Y Capital, alongside other firms including the likes of GL Ventures (affiliated with Hillhouse Capital Group), CICC Capital, and Gaorong Ventures, has separately backed a total of four deals in the month.
Most active investors in China (August 2025)
| Investment company | No. of deals | Total value of participated deals (Million USD) | Lead | Non-lead |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5Y Capital | 4 | 43.5 | 1 | 3 |
| Addor Capital | 3 | 0 | 2 | 1 |
| CAS Star | 3 | 11.5 | 2 | 1 |
| China Merchants Venture Capital Management | 3 | 28 | 2 | 1 |
| CICC Capital | 4 | 43.5 | 1 | 3 |
| Confitop Capital | 3 | 4.5 | 3 | 0 |
| Fortune Capital | 3 | 28 | 3 | 1 |
| Gaorong Ventures | 4 | 43.5 | 1 | 3 |
| GL Ventures (affiliated with Hillhouse Capital Group) | 4 | 17 | 3 | 1 |
| GP Capital | 3 | 15.5 | 2 | 1 |
| Hefei Innovation Investment | 3 | 28 | 0 | 3 |
| HongShan Seed Fund (previously Sequoia China Seed Fund) | 3 | 17 | 1 | 2 |
| IDG Capital | 3 | 17 | 3 | 0 |
| Legend Holdings & affiliates | 3 | 42 | 1 | 2 |
| Lightspeed China Partners | 3 | 17 | 2 | 1 |
| Optics Valley Industrial Investment | 3 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Peakvest | 3 | 25.5 | 1 | 2 |
| Qiming Venture Partners | 6 | 75.7 | 4 | 2 |
| YuanBio Venture Capital | 3 | 29.5 | 0 | 3 |
Note: In our monthly analysis for August 2025, we have put together detailed charts of prominent deals, active investors, deal stages, and the most attractive sectors that have bagged the maximum venture dollars in the Greater China region.
Our database only considers deals officially announced by the related investee, investor(s), and/or financial advisor, while information based on market rumours and news reports citing sources is excluded.
For a more detailed analysis, and to enable comparison between primary and secondary markets, DealStreetAsia has started tracking deals of all sizes since April 2020, as against considering only transactions worth more than $10 million earlier.
We have also introduced a standardised system for industry classification. It currently includes over 50 industries, as well as over 45 new economy and high-tech verticals, which will progressively increase to adapt to local market conditions in our closely watched regions of Greater China, Southeast Asia, and India.
‘In an era of virtual dealmaking, stakeholders tend to be more transparent’ – DFIN’s Peter McMillan
Over half the deals in the next 3 months will be hosted virtually according to 79% of the respondents in DFIN’s DealMaker Meter Survey. Peter McMillan, Head of Sales for APAC at DCIN speaks of the advantages of virtual dealmaking as well as the pitfalls to be avoided, in an exclusive interview with DealStreetAsia
Related Stories
Venture Capital

SEA Deals Barometer Report: Startup funding slumps 84% in Aug
Startup funding in Southeast Asia declined sharply in August, following a record-setting July, as the absence of megadeals pushed the month’s total to the third-lowest so far this year.
Venture Capital

India Deals Barometer Report: Growth investments lift overall startup funding in Aug
Private equity and venture capital investments in Indian startups rebounded to over $1 billion in August, crossing the psycholoicaly-important milestone after slipping below the level in July. The rebound was largely on account of a 3.5x surge in growth-stage investments in the month, which offset a decline in early-stage activity, underscoring investors’ continued caution.



